This is in a nutshell my own condensed analysis of the French universal health care system, combining universal coverage with a public-private mix of hospital and ambulatory care and a higher volume of service provisions than in the United States. It must be understood when studying the French system that universal coverage can thus be achieved without excluding private insurers from the supplementary insurance market.
studying the French system that universal coverage can thus be achieved without excluding private insurers from the supplementary insurance market.
The French health care system was rated the best in the world by the World Health Organization in 2001 while the US health care system ranked 37th. In 2004, France spent 10.5% of its gross domestic product (GDP) and it increased to 11.5% of GDP on health care in 2017. By contrast, the US spent 18% of its GDP on health care in the same year. Payroll taxes in France provide 53% of funding, with employers paying 80% of the tax and employees paying the rest. In addition, a national earmarked income tax contributes 34% of funding, and State subsidies account for 1% of funding.
Universal coverage was achieved over seven decades by extending statutory health insurance (SHI) to all employees (in 1945), retirees (in 1945), the self-employed (in 1966), and the unemployed (in 2000). In 2000, the Couverture maladie universelle (Universal Health Coverage), or CMU, was created for residents not eligible for SHI, although the program required yearly renewals and entitlement changes whenever a beneficiary’s professional or family situation changed. After the implementation of CMU, fewer than 1% of residents were left without baseline coverage.
- Hits: 3903
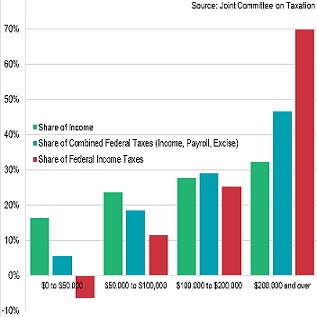 viven.
viven. When there is a stock market crash signaling a recession, stagflation, or severe depression, what we are experiencing is a sudden and very large drop in the value of stocks in the markets, causing a hasty sale of stocks and other securities by investors and some institutions. When the underlying value of the companies that issue the shares suddenly collapses, their price also falls proportionally and the resulting situation is the loss of much of the money that people invested and, in extreme cases, as in the Great Depression of last century, the loss of all your invested capital.
When there is a stock market crash signaling a recession, stagflation, or severe depression, what we are experiencing is a sudden and very large drop in the value of stocks in the markets, causing a hasty sale of stocks and other securities by investors and some institutions. When the underlying value of the companies that issue the shares suddenly collapses, their price also falls proportionally and the resulting situation is the loss of much of the money that people invested and, in extreme cases, as in the Great Depression of last century, the loss of all your invested capital. them, we drink them and we breathe them.
them, we drink them and we breathe them.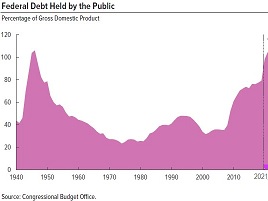 La deuda nacional de Estados Unidos ha sobrepasado ya los 28,7 trillones de dólares (billones en español), lo cual equivale a más de 227 mil dólares por cada contribuyente. Para colmo, el déficit presupuestario superará este año con creces todos los records anteriores (incluso los de tiempos de guerra) por un total de casi 3,2 trillones de dólares, lo cual hará que suba considerablemente el nivel de la deuda. Este déficit representa alrededor del 40% del presupuesto federal, el cual debería reducirse en esa cantidad para equilibrarlo. Por el contrario, se están pasando leyes que añaden gastos por más y más trillones de dólares que el país NO TIENE. Esto significa que el Tesoro deberá expedir más dinero y más instrumentos de deuda, a la vez que idea nuevas fuentes de ingresos impositivos, como ahora se está barajando el de cobrar impuestos a los automóviles según el millaje que recorran cada año.
La deuda nacional de Estados Unidos ha sobrepasado ya los 28,7 trillones de dólares (billones en español), lo cual equivale a más de 227 mil dólares por cada contribuyente. Para colmo, el déficit presupuestario superará este año con creces todos los records anteriores (incluso los de tiempos de guerra) por un total de casi 3,2 trillones de dólares, lo cual hará que suba considerablemente el nivel de la deuda. Este déficit representa alrededor del 40% del presupuesto federal, el cual debería reducirse en esa cantidad para equilibrarlo. Por el contrario, se están pasando leyes que añaden gastos por más y más trillones de dólares que el país NO TIENE. Esto significa que el Tesoro deberá expedir más dinero y más instrumentos de deuda, a la vez que idea nuevas fuentes de ingresos impositivos, como ahora se está barajando el de cobrar impuestos a los automóviles según el millaje que recorran cada año. trillones de dólares que se van sumando a una enorme deuda que le iremos dejando a nuestros hijos, nietos y bisnietos, y que ya nos está afectando con la devaluación del poder adquisitivo del dólar y la resultante inflación.
trillones de dólares que se van sumando a una enorme deuda que le iremos dejando a nuestros hijos, nietos y bisnietos, y que ya nos está afectando con la devaluación del poder adquisitivo del dólar y la resultante inflación.